This post summaries the key points of the article EXPLORING SAFE DISPOSAL OF CO2 AND WASTEWATER IN SALINE AQUIFER, which has been published by authors on the Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 170 (2018) 197-205.
Objective:
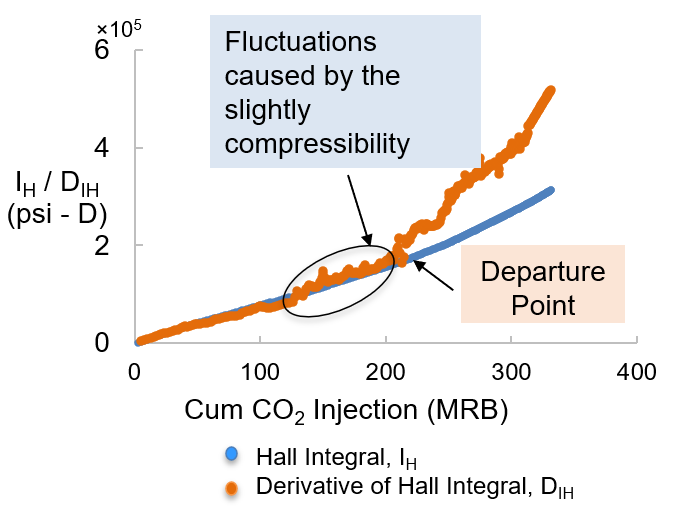
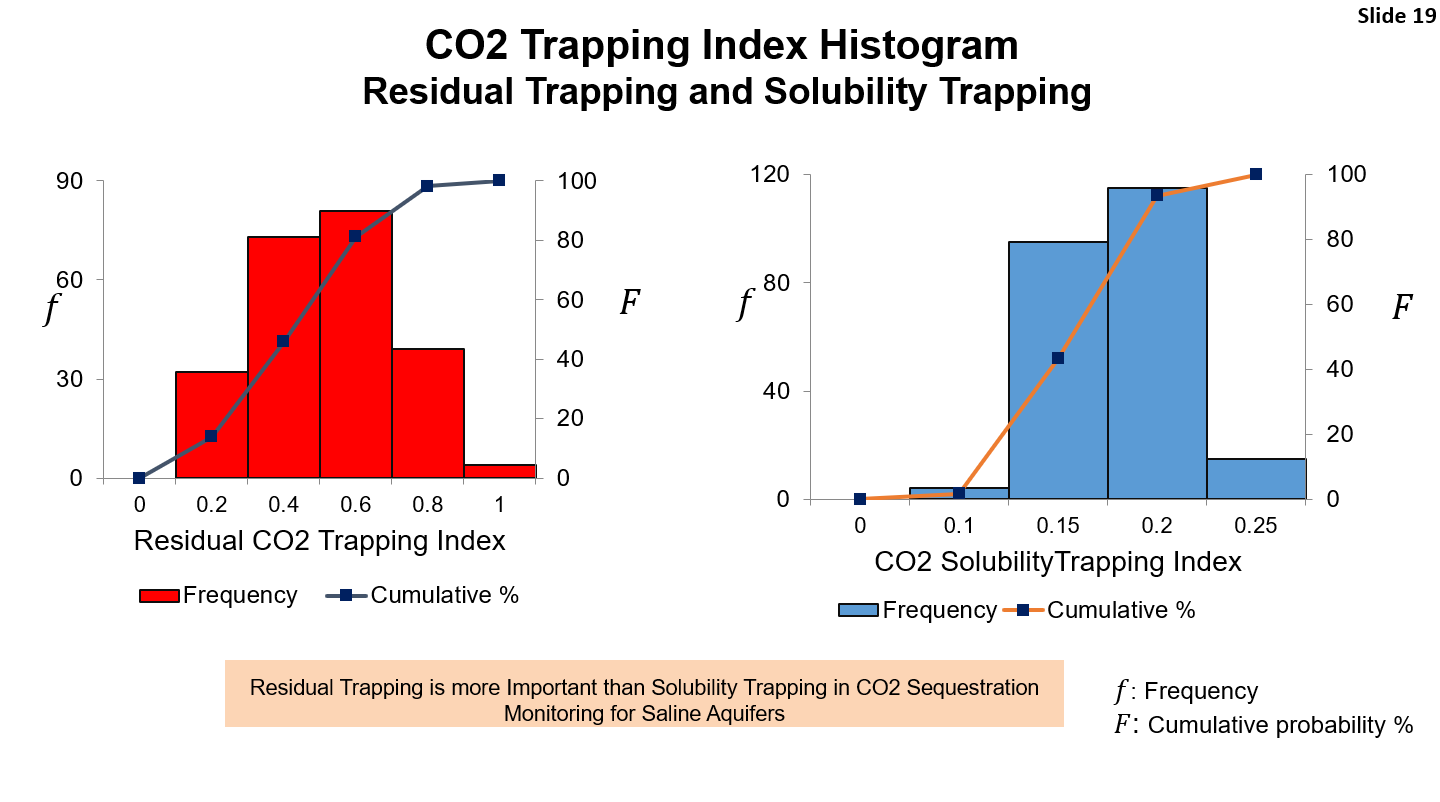
The safe disposal of CO₂ and wastewater in saline aquifers is a critical challenge in both carbon sequestration and oil and gas operations. Our study presents a systematic approach to monitoring injection-well performance using real-time diagnostics and probabilistic modeling. The modified-Hall analysis proved essential for detecting abnormal injection behavior, enabling safe disposal practices. Key factors influencing injection efficiency include aquifer heterogeneity, rock compressibility, and fracture gradient. We found that safe pore-volume injection in saline aquifers is approximately 1.6% for wastewater and 1.5% for CO₂, with an 80% probability. Additionally, CO₂ trapping mechanisms such as residual and solubility trapping were analyzed, highlighting the role of critical gas saturation and brine salinity in storage efficiency. This research provides valuable insights for optimizing injection operations and ensuring environmental safety.
Methodology:
Utilized probabilistic modeling and modified-Hall analysis to assess injection performance and detect abnormalities.
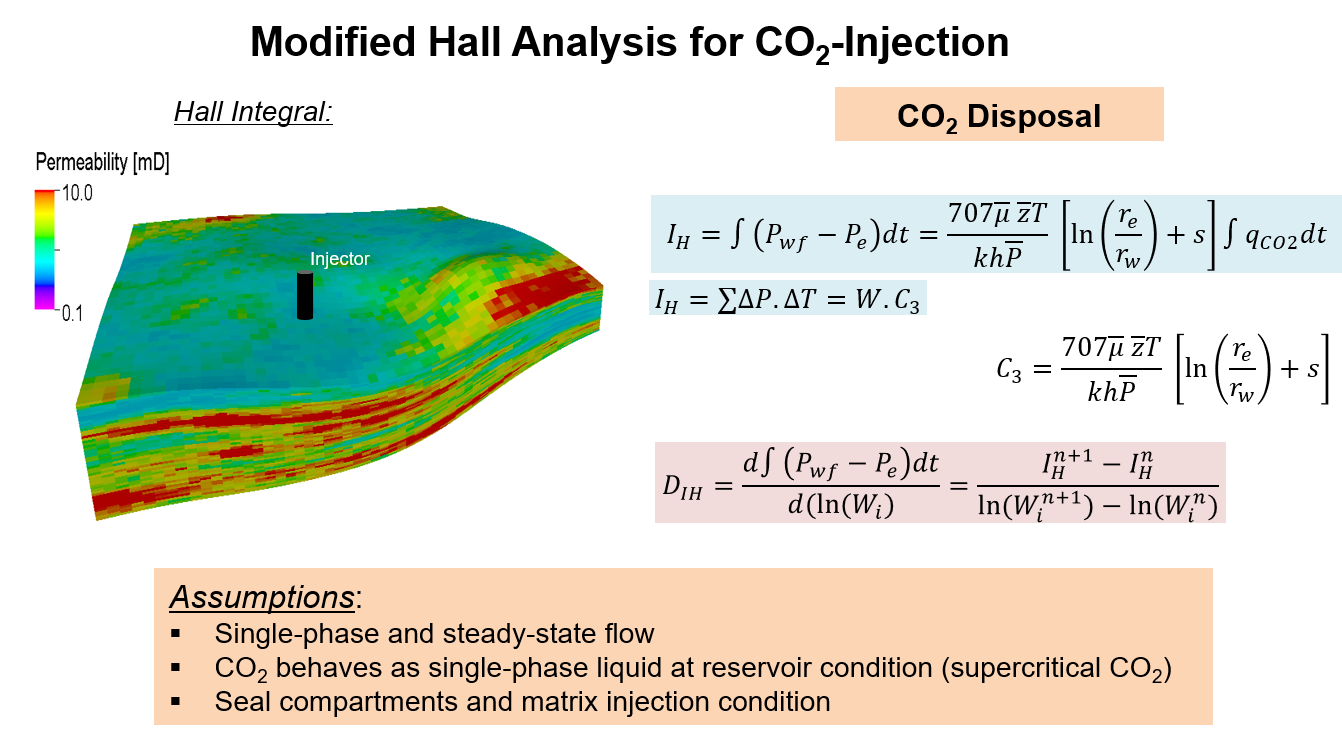
Key Findings:
💡 Cite my publication:
Tien Phan, Maulin Gogri, Shah Kabir, Zulfiquar Reza. EXPLORING SAFE DISPOSAL OF CO2 AND WASTEWATER IN SALINE AQUIFER. J. Petrol. Science and Engineering 170 (2018) 197-205.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2018.06.065